Estimating what you gain or lose in SEO ranking
To understand the importance of SEO work it is necessary for you to understand how much you stand to gain or lose through search ranking. To help you estimate how much traffic you may stand to gain or lose by moving up or down in the search engine rankings, the first thing you’ll need to review would be the concept of Click Distribution by SERP Ranking. This basically refers to how user’s clicks are distributed throughout the Top 10 SERP rankings.
If you recall, there are limited data sets available within the search industry regarding the distribution of clicks. I’ve taken the liberty of averaging all of the known data sets together in an effort to consolidate the percentages into one percentage. Here’s what I came up with for the click distribution percentages in SERP results.
- Position #1: 45.46% of all clicks
- Position #2: 15.69% of all clicks
- Position #3: 10.09% of all clicks
- Position #4: 5.49% of all clicks
- Position #5: 5.00% of all clicks
- Position #6: 3.94% of all clicks
- Position #7: 2.51% of all clicks
- Position #8: 2.94% of all clicks
- Position #9: 1.97% of all clicks
- Position #10: 2.71% of all clicks
Total: 95.91% of all clicks occur on Page #1 of SERPs
SERP Rankings, Search Volume, and Click Distribution
Lets follow this logic…by monitoring your search rankings, examining search volume, and applying the distribution percentages you can begin to get an idea of how much traffic you’re likely to receive based on where you rank within the search engines.
Lets work on an example. In our example, we’ll say that you’re a nationally prominent seller of dog supplies. Over the past few years you’ve worked really hard and are now ranking #10 for the term “dog supplies.”
By using the Google Adwords Keyword Tool, you’ll see that the key term “dog supplies” receives 74,000 Global Monthly Searches.

This is the first place where it gets a little tricky. Which search volume number do you use? This depends on your business type and how realistic you wish to be about the quality of your traffic.
If you’re a global brand like Petco or Petsmart then its safe to say you should use the Global Search Volume number. However, if you’re brand is more local within your country, you should go with the Local Monthly Search Volume (Note: Your Local Monthly Search Volume constitues the search volume generated by your country, in my case the United States).
Now, lets apply our initial logic.
“Dog supplies” generates 74,000 global monthly searches and we’re currently (fictionally) ranking #10. Based on our original click distribution percentages, we should receive 2.71% of all clicks. If that’s the case, we should currently be getting approximately (carry the one, minus the blah blah) 2,005 visits. That’s 74,000 x 0.0271. Make sense?
Now, lets make another connection. Let’s imagine that you’ve worked really really hard – built your links, ate your spinach, said your prayers – and achieved the #1 ranking for the term “dog supplies!” Good work.
Based on the percentages, we’ll now take 74,000 and multiply it by 0.4546. This SERP position should give us approximately 33,640 visits. That’s a big jump in traffic and clearly shows you how valuable the #1 position can be in terms of gaining additional traffic. But how much did you gain?
Okay, let’s put this last piece together. Take 33,640 visits minus 2,005 visits and you’ll see that you stand to gain 31,635 additional visits by moving from position #10 to #1.
Quickly, let’s apply this logic backwards. Let’s say you’re ranking #3 and slip to #6. At the #3 position you should expect around 7,467 visits. At position #6, you should expect around 2,916 visits. That’s a slip of 4,551 visits! That’s a lot to lose and can be the difference in gaining or losing a lot of web revenue/exposure.
The Flaws in this Logic
Now here’s the disclaimer. The above logic is flawed. It assumes that every search result is absolutely perfect and only includes the 10 organic listings – nothing else. We know that’s false.
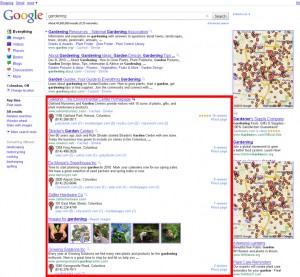
The search results of this day and age are what I like to call “muddy.” The reason I call them Muddy SERPs is that there are so many different types of results that are injected right into the natural results that may draw a click away and water down the click percentages (local, news, social, etc).
Here is an example of a Muddy SERP result:
In addition, there are different types of searches. Different search contexts certainly impact the patterns in which people click around the SERPs, which in turn may affect the click distribution percentages.
Different types of search classifications is discussed in detail by Aaron Wall over at SEOBook. These types are Navigational, Transactional, and Informational.
- In general, for navigational searches people click the top result more often than they would on an informational search.
- In general, for informational searches people tend to click throughout the full set of search results at a more even distribution than they would for navigational or transactional searches.
- The only solid recently-shared publicly data on those breakdowns is from Dogpile, a meta search engine. But given how polluted meta search services tend to be (with ads mixed in their search results) those numbers were quite a bit off from what one might expect. And once more, they are aggregate numbers.
Another thing that may affect how the numbers that Google may not show are the number of searches that don’t result in a click. With the new Google Instant Search feature, I know that many of my searches are abandoned quickly without a click if I don’t see what I need right away. This type of behavior may not take place on the other two major search engines, but Google is ahead of the curve in this regard.
The Smartest Thing To Do
The best thing you can do is knock at least 30% off of whatever number you have, and then you may have a more accurate estimate of the real traffic that may come in by being at a certain position.
So with that logic we’ll re-approach our original example. Remember, we were ranking #10 in which we were garnering 2,005 visits. Remember, we moved to the #1 position which represented 33,640 visits.
Let’s slice 30% right off of both of those numbers. The #10 ranking will probably garner closer to 1,404 visits rather than the original estimate of 2,005 visits. Likewise, the #1 ranking will probably pull in something closer to 23,548 visits rather than our original estimate of 33,640 visits.
This means that you ultimately stand to gain around 22,144 visits per month by moving from the #10 SERP result to the #1 SERP for the term “dog supplies.”
There it is! You’ve done it. You can apply this logic – however flawed – going forward to attempt to estimate traffic gains/losses by fluctuations in SERP rank.
Tags: google instant, Internet Marketing, search engine marketing, SEO tips